Configuration¶
Command Line Options¶
Locust is configured mainly through command line arguments.
$ locust --help
Usage: locust [options] [UserClass ...]
Common options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f <filename>, --locustfile <filename>
The Python file or module that contains your test,
e.g. 'my_test.py'. Accepts multiple comma-separated
.py files, a package name/directory or a url to a
remote locustfile. Defaults to 'locustfile'.
--config <filename> File to read additional configuration from. See https:
//docs.locust.io/en/stable/configuration.html#configur
ation-file
-H <base url>, --host <base url>
Host to load test, in the following format:
https://www.example.com
-u <int>, --users <int>
Peak number of concurrent Locust users. Primarily used
together with --headless or --autostart. Can be
changed during a test by keyboard inputs w, W (spawn
1, 10 users) and s, S (stop 1, 10 users)
-r <float>, --spawn-rate <float>
Rate to spawn users at (users per second). Primarily
used together with --headless or --autostart
-t <time string>, --run-time <time string>
Stop after the specified amount of time, e.g. (300s,
20m, 3h, 1h30m, etc.). Only used together with
--headless or --autostart. Defaults to run forever.
-l, --list Show list of possible User classes and exit
--config-users [CONFIG_USERS ...]
User configuration as a JSON string or file. A list of
arguments or an Array of JSON configuration may be
provided
Web UI options:
--web-host <ip> Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to '*'
(all interfaces)
--web-port <port number>, -P <port number>
Port on which to run web host
--headless Disable the web interface, and start the test
immediately. Use -u and -t to control user count and
run time
--autostart Starts the test immediately (like --headless, but
without disabling the web UI)
--autoquit <seconds> Quits Locust entirely, X seconds after the run is
finished. Only used together with --autostart. The
default is to keep Locust running until you shut it
down using CTRL+C
--web-login Protects the web interface with a login page. See
https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/extending-
locust.html#authentication
--tls-cert <filename>
Optional path to TLS certificate to use to serve over
HTTPS
--tls-key <filename> Optional path to TLS private key to use to serve over
HTTPS
--class-picker Enable select boxes in the web interface to choose
from all available User classes and Shape classes
--legacy-ui Use the legacy frontend for the web UI (deprecated,
support will be removed soon)
Master options:
Options for running a Locust Master node when running Locust distributed. A Master node need Worker nodes that connect to it before it can run load tests.
--master Launch locust as a master node, to which worker nodes
connect.
--master-bind-host <ip>
IP address for the master to listen on, e.g
'192.168.1.1'. Defaults to * (all available
interfaces).
--master-bind-port <port number>
Port for the master to listen on. Defaults to 5557.
--expect-workers <int>
Delay starting the test until this number of workers
have connected (only used in combination with
--headless/--autostart).
--expect-workers-max-wait <int>
How long should the master wait for workers to connect
before giving up. Defaults to wait forever
--enable-rebalancing Re-distribute users if new workers are added or
removed during a test run. Experimental.
Worker options:
Options for running a Locust Worker node when running Locust distributed.
Typically ONLY these options (and --locustfile) need to be specified on workers, since other options (-u, -r, -t, ...) are controlled by the master node.
--worker Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as worker. Can be combined with setting
--locustfile to '-' to download it from master.
--processes <int> Number of times to fork the locust process, to enable
using system. Combine with --worker flag or let it
automatically set --worker and --master flags for an
all-in-one-solution. Not available on Windows.
Experimental.
--master-host <hostname>
Hostname of locust master node to connect to. Defaults
to 127.0.0.1.
--master-port <port number>
Port to connect to on master node. Defaults to 5557.
Tag options:
Locust tasks can be tagged using the @tag decorator. These options let specify which tasks to include or exclude during a test.
-T [<tag> ...], --tags [<tag> ...]
List of tags to include in the test, so only tasks
with at least one matching tag will be executed
-E [<tag> ...], --exclude-tags [<tag> ...]
List of tags to exclude from the test, so only tasks
with no matching tags will be executed
Request statistics options:
--csv <filename> Store request stats to files in CSV format. Setting
this option will generate three files:
<filename>_stats.csv, <filename>_stats_history.csv and
<filename>_failures.csv. Any folders part of the
prefix will be automatically created
--csv-full-history Store each stats entry in CSV format to
_stats_history.csv file. You must also specify the '--
csv' argument to enable this.
--print-stats Enable periodic printing of request stats in UI runs
--only-summary Disable periodic printing of request stats during
--headless run
--reset-stats Reset statistics once spawning has been completed.
Should be set on both master and workers when running
in distributed mode
--html <filename> Store HTML report to file path specified
--json Prints the final stats in JSON format to stdout.
Useful for parsing the results in other
programs/scripts. Use together with --headless and
--skip-log for an output only with the json data.
Logging options:
--skip-log-setup Disable Locust's logging setup. Instead, the
configuration is provided by the Locust test or Python
defaults.
--loglevel <level>, -L <level>
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL.
Default is INFO.
--logfile <filename> Path to log file. If not set, log will go to stderr
Other options:
--show-task-ratio Print table of the User classes' task execution ratio.
Use this with non-zero --user option if some classes
define non-zero fixed_count attribute.
--show-task-ratio-json
Print json data of the User classes' task execution
ratio. Use this with non-zero --user option if some
classes define non-zero fixed_count attribute.
--version, -V Show program's version number and exit
--exit-code-on-error <int>
Sets the process exit code to use when a test result
contain any failure or error. Defaults to 1.
-s <number>, --stop-timeout <number>
Number of seconds to wait for a simulated user to
complete any executing task before exiting. Default is
to terminate immediately. This parameter only needs to
be specified for the master process when running
Locust distributed.
--equal-weights Use equally distributed task weights, overriding the
weights specified in the locustfile.
User classes:
<UserClass1 UserClass2>
At the end of the command line, you can list User
classes to be used (available User classes can be
listed with --list). LOCUST_USER_CLASSES environment
variable can also be used to specify User classes.
Default is to use all available User classes
Examples:
locust -f my_test.py -H https://www.example.com
locust --headless -u 100 -t 20m --processes 4 MyHttpUser AnotherUser
See documentation for more details, including how to set options using a file or environment variables: https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/configuration.html
Environment Variables¶
Options can also be set through environment variables. They are typically the same as the command line argument
but capitalized and prefixed with LOCUST_:
On Linux/macOS:
$ LOCUST_LOCUSTFILE=custom_locustfile.py locust
On Windows:
> set LOCUST_LOCUSTFILE=custom_locustfile.py
> locust
Configuration File¶
Options can also be set in a configuration file in the config or TOML file format.
Locust will look for ~/.locust.conf, ./locust.conf and ./pyproject.toml by default.
You can specify an additional file using the --config flag.
$ locust --config custom_config.conf
Here’s a quick example of the configuration files supported by Locust:
locust.conf¶
locustfile = locust_files/my_locust_file.py
headless = true
master = true
expect-workers = 5
host = https://target-system
users = 100
spawn-rate = 10
run-time = 10m
tags = [Critical, Normal]
pyproject.toml¶
When using a TOML file, configuration options should be defined within the [tool.locust] section.
[tool.locust]
locustfile = "locust_files/my_locust_file.py"
headless = true
master = true
expect-workers = 5
host = "https://target-system"
users = 100
spawn-rate = 10
run-time = "10m"
tags = ["Critical", "Normal"]
Note
Configuration values are read (and overridden) in the following order:
~/.locust.conf -> ./locust.conf -> ./pyproject.toml -> (file specified using --conf) -> env vars -> cmd args
All available configuration options¶
Here’s a table of all the available configuration options, and their corresponding Environment and config file keys:
Command line |
Environment |
Config file |
Description |
|
|
|
The Python file or module that contains your test, e.g. ‘my_test.py’. Accepts multiple comma-separated .py files, a package name/directory or a url to a remote locustfile. Defaults to ‘locustfile’. |
|
|
|
Host to load test, in the following format: https://www.example.com |
|
|
|
Peak number of concurrent Locust users. Primarily used together with –headless or –autostart. Can be changed during a test by keyboard inputs w, W (spawn 1, 10 users) and s, S (stop 1, 10 users) |
|
|
|
Rate to spawn users at (users per second). Primarily used together with –headless or –autostart |
|
|
|
Stop after the specified amount of time, e.g. (300s, 20m, 3h, 1h30m, etc.). Only used together with –headless or –autostart. Defaults to run forever. |
|
|
|
User configuration as a JSON string or file. A list of arguments or an Array of JSON configuration may be provided |
|
|
|
Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to ‘*’ (all interfaces) |
|
|
|
Port on which to run web host |
|
|
|
Disable the web interface, and start the test immediately. Use -u and -t to control user count and run time |
|
|
|
Starts the test immediately (like –headless, but without disabling the web UI) |
|
|
|
Quits Locust entirely, X seconds after the run is finished. Only used together with –autostart. The default is to keep Locust running until you shut it down using CTRL+C |
|
|
|
Protects the web interface with a login page. See https://docs.locust.io/en/stable/extending-locust.html#authentication |
|
|
|
Optional path to TLS certificate to use to serve over HTTPS |
|
|
|
Optional path to TLS private key to use to serve over HTTPS |
|
|
|
Enable select boxes in the web interface to choose from all available User classes and Shape classes |
|
|
|
Use the legacy frontend for the web UI (deprecated, support will be removed soon) |
|
|
|
Launch locust as a master node, to which worker nodes connect. |
|
|
|
IP address for the master to listen on, e.g ‘192.168.1.1’. Defaults to * (all available interfaces). |
|
|
|
Port for the master to listen on. Defaults to 5557. |
|
|
|
Delay starting the test until this number of workers have connected (only used in combination with –headless/–autostart). |
|
|
|
How long should the master wait for workers to connect before giving up. Defaults to wait forever |
|
|
|
Set locust to run in distributed mode with this process as worker. Can be combined with setting –locustfile to ‘-‘ to download it from master. |
|
|
|
Number of times to fork the locust process, to enable using system. Combine with –worker flag or let it automatically set –worker and –master flags for an all-in-one-solution. Not available on Windows. Experimental. |
|
|
|
Hostname of locust master node to connect to. Defaults to 127.0.0.1. |
|
|
|
Port to connect to on master node. Defaults to 5557. |
|
|
|
List of tags to include in the test, so only tasks with at least one matching tag will be executed |
|
|
|
List of tags to exclude from the test, so only tasks with no matching tags will be executed |
|
|
|
Store request stats to files in CSV format. Setting this option will generate three files: <filename>_stats.csv, <filename>_stats_history.csv and <filename>_failures.csv. Any folders part of the prefix will be automatically created |
|
|
|
Store each stats entry in CSV format to _stats_history.csv file. You must also specify the ‘–csv’ argument to enable this. |
|
|
|
Enable periodic printing of request stats in UI runs |
|
|
|
Disable periodic printing of request stats during –headless run |
|
|
|
Reset statistics once spawning has been completed. Should be set on both master and workers when running in distributed mode |
|
|
|
Store HTML report to file path specified |
|
|
|
Disable Locust’s logging setup. Instead, the configuration is provided by the Locust test or Python defaults. |
|
|
|
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL. Default is INFO. |
|
|
|
Path to log file. If not set, log will go to stderr |
|
|
|
Sets the process exit code to use when a test result contain any failure or error. Defaults to 1. |
|
|
|
Number of seconds to wait for a simulated user to complete any executing task before exiting. Default is to terminate immediately. This parameter only needs to be specified for the master process when running Locust distributed. |
Running without the web UI¶
Using multiple Locustfiles at once¶
The -f/--locustfile option accepts a single directory of locustfiles as an option. Locust will recursively
search the directory for *.py files, ignoring files that start with “_”.
Example:
With the following file structure:
├── locustfiles/
│ ├── locustfile1.py
│ ├── locustfile2.py
│ └── more_files/
│ ├── locustfile3.py
│ ├── _ignoreme.py
$ locust -f locustfiles
Locust will use locustfile1.py, locustfile2.py & more_files/locustfile3.py
Additionally, -f/--locustfile accepts multiple, comma-separated locustfiles.
Example:
$ locust -f locustfiles/locustfile1.py,locustfiles/locustfile2.py,locustfiles/more_files/locustfile3.py
Locust will use locustfile1.py, locustfile2.py & more_files/locustfile3.py
You can also use -f/--locustfile for web urls. This will download the file and use it as any normal locustfile.
Example:
$ locust -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/locustio/locust/master/examples/basic.py
Running Locust with User class UI picker¶
You can select which Shape class and which User classes to run in the WebUI when running locust with the --class-picker flag.
No selection uses all of the available User classes.
Example:
With the following file structure:
├── src/
│ ├── some_file.py
├── locustfiles/
│ ├── locustfile1.py
│ ├── locustfile2.py
│ └── more_files/
│ ├── locustfile3.py
│ ├── _ignoreme.py
│ └── shape_classes/
│ ├── DoubleWaveShape.py
│ ├── StagesShape.py
$ locust -f locustfiles --class-picker
The Web UI will display:
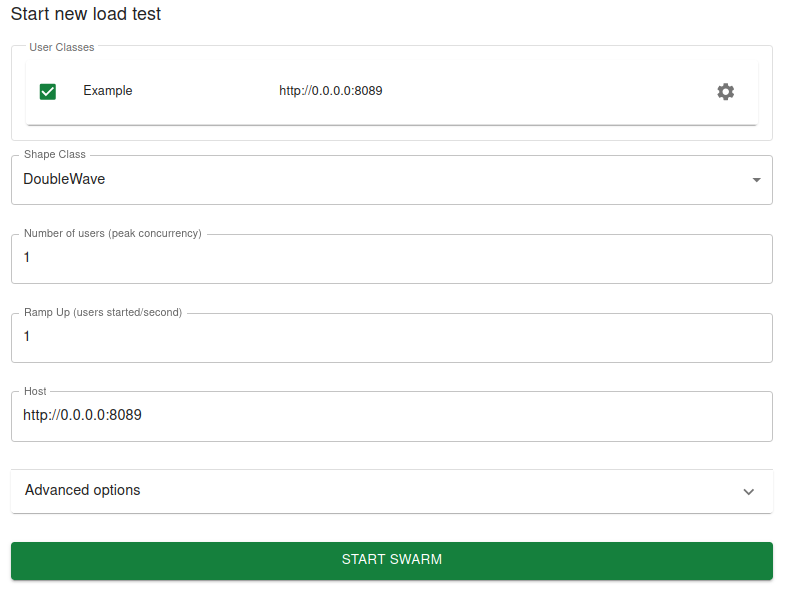
With the new --modern-ui, the class picker will addtionally allow for configuring any settings for each selected user.
This includes selecting tasks, configuring the weight or fixed count, and configuring the host.
It is even possible to add custom arguments that you wish to be configurable for each user. Simply add a json classethod
to your user:
class Example(HttpUser):
@task
def example_task(self):
self.client.get(f"/example/{self.some_custom_arg}")
@classmethod
def json(self):
return {
"host": self.host,
"some_custom_arg": "example"
}
Configuration for the User classes¶
You can configure any settings you may wish for each user on the command line, the same as you may in the modern UI.
Using the --config-users argument, you may pass a JSON string or file with your user configuration. To configure
multiple users you pass multiple arguments to --config-users or use a JSON Array.
Each user settings object must contain a key user_class_name. This key corresponds to the class that you wish
to configure.
Example:
$ locust --config-users '{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1}'
$ locust --config-users '[{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1}, {"user_class_name": "ExampleTwo", "fixed_count": 2}]'
$ locust --config-users '{"user_class_name": "Example", "fixed_count": 1}' '{"user_class_name": "ExampleTwo", "fixed_count": 2}'
$ locust --config-users config_users.json
Custom arguments¶
See Custom arguments
Customization of statistics settings¶
Default configuration for Locust statistics is set in constants of stats.py file. It can be tuned to specific requirements by overriding these values. To do this, import locust.stats module and override required settings:
import locust.stats
locust.stats.CONSOLE_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC = 15
It can be done directly in Locust file or extracted to separate file for common usage by all Locust files.
The list of statistics parameters that can be modified is:
Parameter name |
Purpose |
STATS_NAME_WIDTH |
Width of column for request name in console output |
STATS_TYPE_WIDTH |
Width of column for request type in console output |
CSV_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC |
Interval for how frequently the CSV file is written if this option is configured |
CONSOLE_STATS_INTERVAL_SEC |
Interval for how frequently results are written to console |
CURRENT_RESPONSE_TIME_PERCENTILE_WINDOW |
Window size/resolution - in seconds - when calculating the current response time percentile |
PERCENTILES_TO_REPORT |
List of response time percentiles to be calculated & reported |
PERCENTILES_TO_CHART |
List of response time percentiles in the screen of chart for Web UI |
MODERN_UI_PERCENTILES_TO_CHART |
List of response time percentiles in the screen of chart for the modern Web UI |
PERCENTILES_TO_STATISTICS |
List of response time percentiles in the screen of statistics for Web UI This parameter supports only modern UI |